How Does Google Rank Your Website In 2022
Owning or managing a kitchen bedroom or bathroom retailer you no doubt have checked to see how your own site ranks for certain search terms. Here we’re going to try and give you an understanding of how Google ranks these sites and therefore some insight into what you need to do rank higher in 2021.
Tl;dr (too long didn’t read it)
If you just want the executive summary, here it is. Make sure your site is fast and mobile responsive. Learn about Web Core Vitals- they are increasingly important. If your site isn’t https (i.e. hasn’t got an SSL certificate) get one. Try and produce some high-quality content, well written, expansive with quality imagery. If you’re not able to invest the time in learning the basics of SEO- on and off page, get an agency to do it or prepare to be demoted into the irrelevance of page three. Schema works, and your GMB business reviews matter so curate them. If your site is brand new, prepare for some hard yards, get busy and be patient.
How Google won the internet:
Think about this for a second, Google’s product is search quality. When we search for something- we’ve come to expect immediate, high quality results that reflect our semantic intent… even when we are lazy and parsed our search term to just a few, maybe misspelt words.
Remember the early days of the internet- when you had to search through garbage on Alta Vista to find what you wanted? That’s what Google solved and it is how it won the internet. Google won by quality; they produced better results for users who flocked to their search tools in their billions. Google is still motivated by quality. They want to return search results that are useful, authoritative, trustworthy, and frustration free whilst delivering excellent user experience. If they serve up sites that achieve those aims, people keep coming back for more. If you’re getting visitors from Google without doing those things, it isn’t because Google likes you, it’s because it dislikes your competitors more. That isn’t a recipe for long term success on Google.
There are an awful lot of factors (believed to be more than 200) that Google’s proprietary algorithm uses to rank websites. Let’s go back to that word proprietary. Google’s search algo is their secret sauce; in that way it is like the Colonel’s secret recipe for KFC or AG Barr’s concoction for Irn Bru… if fried chicken and fizzy pop were worth more than a trillion dollars. So, let’s be clear; nobody outside of google, and very, very few within it, know exactly what ranking factors Google uses or the weighting of those. That being said, Search Engine Optimisation experts have a good working understanding based on what Google has said, their published guidance and documentation, and through experimentation and experience.
So given there are hundreds of factors, and some are pretty esoteric (EXIF data in UGC uploads to GMB profiles anyone) We’ll focus on the ones that we’re confident make the biggest difference.
- Security
- User Experience/ Speed
- Content
- Backlink profile
- Domain age
- Technical SEO
- Schema
- GMB Signals
The theory is this- do these things better than your competitors and you’ll have a very good shot at beating them in the rankings. But remember a couple of things- one, your competitors in this sense mean any another website ranking for the same term you want to rank for. So that could be Houzz, Ideal Home, Miele… not just who you think your competitors are. Two, doing something badly actually harms you- like not having a secure site, or not having a mobile friendly site. View fixing these things are prerequisites to achieving better rankings.
Without further ado, here we go- how to win on Google:
Security
HTTPS via HTTP. People it’s 2021. Unsecured, a third party can intercept the communication between your webserver and a visitor’s device. There is no excuse for not having a valid SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificate on your website. Google takes privacy seriously, and so should you. You can check this on the address bar of your browser. If the web address is preceded by a padlock and the letters ‘https’- you’re secure.
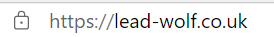
This is what you want to see.
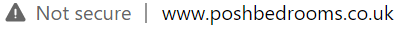
If you see this, sort it out.
Mobile friendliness of websites.
Remember way back in 2014 when large parts of the internet were difficult to navigate on a mobile phone? Well unfortunately that issue persists. Common errors are text that is too small, clickable elements spaced too close together, content exceeds the max width of the device meaning the user has to try and slide around their finger to see the content. Google has a mobile friendly testing tool. Mobile-Friendly Test – Google Search Console
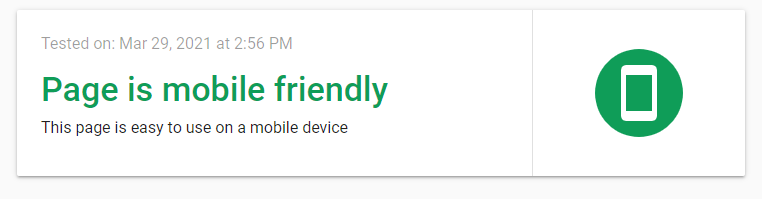
If your page passed this test it is mobile friendly and, as such will get more ranking credit for this ranking factor than sites that fail. If your site failed, remember most search is no on mobile. You need to get this fixed.
Speed and user experience
Fast sites that users find easy to navigate, frustration free, create happy users. Both Google and site owners should hate ‘bounces’. These are visitors that click to your site and then leave without interacting with the site at all. High bounce rates indicate Google has failed in its mission to deliver quality. If a bounce had verbal meaning, it would be, ‘I’ll pass, show me something else.’ It’s a vote of no confidence in your site and Google is listening.
So how fast does your site need to be? Check out this information on bounce rates by page load speed as produced by Google themselves:
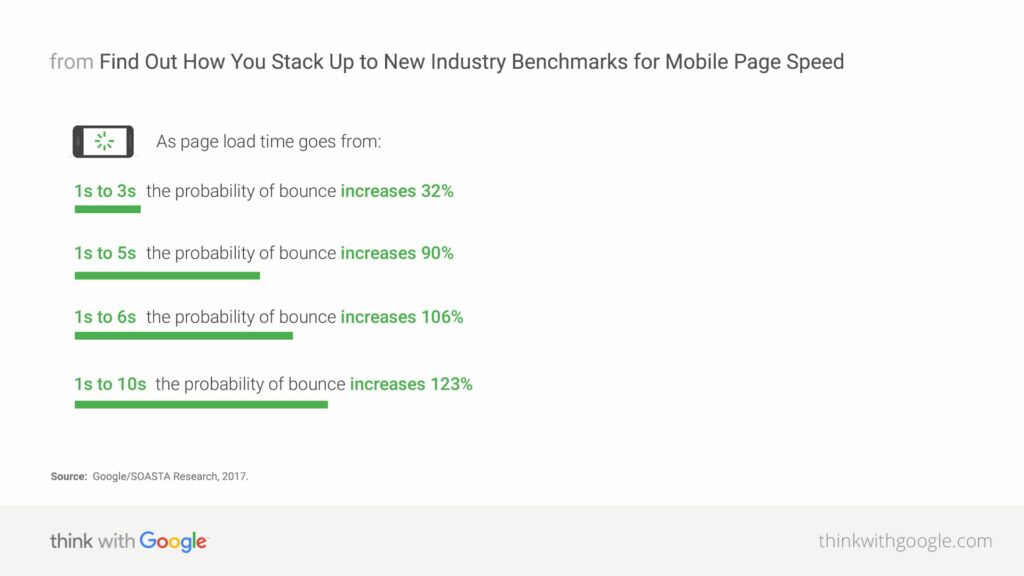
Just look at the impact of speed on bounce rate. You can’t afford to lose these visitors and Google hates you for being slow. Google also has some data on conversion- not the topic of this article but slow sites can convert more than 95% less well than fast ones.
Web core vitals
In May 2021 Google released its ‘Web Core Vitals’ update into the wild, trying to combine speed and some key useability benchmarks into an algo update that is the most explicit they’ve ever been about an update. The three tests are:
- Largest Contentful Paint
- First Input Delay
- Cumulative Layout Shift
This is Google’s way of saying to webmasters, ‘hey, we want faster, frustration free sites and we’ll reward the sites that do so with better rankings.’ It is a message you should receive loud and clear.
These benchmark tests relate to how fast your pages load, how quickly the site responds to user inputs, and how much your content layout moves about during loading. (ever tried to click something, it moves, and you click the wrong thing? Exactly)
Taken together these tests are now critical. You can read all about them and how to test for them here: Web Vitals.
Other user experience signals
Many experienced search professionals believe Google will use data like average time on site/ repeat visits etc as proxies for user experience (which stands to reason as the more time you spend on a website the more likely you are finding it useful). The key takeaway is the better your user experience (think how easily people can find their away around and find what they are looking for) the better.
Content
Google ranks pages not websites. The content of the page you want to rank is key to achieving a ranking for any given search term. The better quality the content, the better chance of it ranking. So what makes content high quality?
Relevance, depth, originality, readability, structure, multimedia… and more.
Your content needs to be relevant to the search query that triggered the search report. The more relevant the better. If you’ve taken the time to explore in detail the topic, researched it and written content that covers the topic in a lot of depth, that is content primed to rank. If it’s thin, only tangentially relevant or poorly written- its far less likely to rank.
Content length matters. Whilst Google isn’t explicit about this, there is plenty of research showing that there is a relationship between content length and ranking. Top ranking content typically has more than 2,000 words.
If you want to rank for a search term like ‘farmhouse kitchens’ you’re going to need to start with brain storming your headings. What are the materials, layout options, work surfaces and appliances people might use in this type of design? What are your recommended ancillary finishes for floors, walls and ceilings? How about soft furnishings and accessories? Could you interview any of your designers or external designers for their top tips? What should you avoid? What’s on trend in 2021? What’s gone cold in 2021? If you’re adding value to the online conversation, you’re on the right track.
Content isn’t just written of course, you’ll no doubt have imagery on the page. Beyond being optimised to reduce file size and minimise the impact of images on page loading speed, this imagery needs clues for Google to understand what it is. This involves titling your imagery in a way google understands and providing ‘image alt tags’ to describe the image. The same applies to video, if you’ve embedded it from YouTube make sure the descriptors for the video in YouTube are complete and the link from YouTube is to your page, so you get the credit for it.
Backlinks
Backlinks are links from other websites to yours. To understand why they are important, we need a brief trip back in time to the foundations of Google. Basically, the founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin developed an understanding that links from one page to another on the web could be thought of as votes- but not at all votes were equal. Their inspiration was academic papers and the citations contained within them. As an example, if you knew nothing other than the fact Einstein’s paper on his theory of relativity has been cited 3,804 times by other physicist’s published papers, you’d know it was pretty important- and because you knew it was other physicists citing it, you’d know it was pretty important in the world of physics. Now imagine that Einstein cited another paper- his vote on the topic could be considered a lot more authoritative than most other peoples- hence not all votes being equal and some being worth more. Here is an excellent overview of this remarkable invention The Birth of Google | WIRED)
The Google founders took this understanding and applied it to search- and what do you know, it worked. Since then, this original theory has been developed and redeveloped, but what remains relevant is that backlinks from authoritative websites in your niche, for example Apartment Therapy or the Design Sheppard remain important to building your rankings.
The practice of trying to develop these links is called backlink building. Some of these are relatively easy to get such as a directory listing for your business category and physical address. Others are far harder, editorially reviewed such as the two listed above. Both are useful, but Apartment Therapy and Design Sheppard are likely to be far more so. Links from dodgy looking sites, sites that look very spammy etc can harm your ranking, so be cautious where you try to get links from.
The bad news about links
for some search terms you’re competing for ranking against big businesses like Magnet or Hammonds who have a team of people doing this type of thing. You’re also competing against the like of Apartment Therapy who at the time of writing had 7.1m links from 80,501 different websites.
When deciding what to write about, pick battles you can win. You could spend days writing an article about ‘kitchens’ and you’ll likely get nowhere- because your backlink profile just can’t win an arm wrestle with seven million links.
Domain age
Matt Cutts of Google has said that google doesn’t care about the age of your domain. I’ve yet to meet an experienced SEO who believes this. We at Lead Wolf have seen time and again how difficult it is to rank brand new domains. It can take months, maybe more. If yours is a new domain there is little you can do about this beyond trying to accelerate your other ranking factors to outweigh this problem- as well as some small mitigation strategies you can try like making sure your domain is registered with Google, make sure your GMB profile is verified, spend some money with Google Ads etc- these all help them verify you as a real business.
Technical SEO
Like much of this article, you could fill a book just on this topic. It’s either something you’re prepared to become pretty expert in- or you delegate to an agency- or you just choose to ignore, perhaps at your peril. The main concepts cover the correct use of page titles, urls, headings, canonicals, meta descriptions, understanding what is your ‘pillar content’ and organising an internal linking strategy to reflect it. This ‘on page’ work is important. It helps inform Google about your content, disambiguate any difficulty Google is having discerning between pages on your site and understand the relative importance of a particular page. There is an enormous amount of information on this on the web you can find by googling ‘on page SEO.’
Schema
Schema in this sense refers to structured data. It is machine readable text organised by categorisation using a particular format that a machine (in this case Google’s algo) can understand. The advantage of this is you use it to specifically inform Google about your business or aspects of it. What/ where/ when/ Whom etc can all be conveyed via Schema in a way we know Google understands. More specifically you can select specific types of Schema to inform Google about particular aspects of your business. For example, you can use event schema to tell Google about an event in the showroom, perhaps a chef event etc. Here is an example of a Schema type you’d use to convey this information. Event – Schema.org Type
Of course knowing what Schema is and when to use it isn’t the same being able to use it. For that you’ll need a Schema generator that outputs the Schema code you’ll include on the relevant page of your website. This is probably one for experts- so if you want to know more, please get in touch with us.
Social links and signals
Reviews on your Google My Business page are ranking factors for search results with a local intent. For example, someone searching for ‘Bathroom Showrooms near me’ is going to see results (both in the map ranking and just in search rankings) that are impacted by reviews. This is a complex area, and you can read a lot more about it in our guide to Google My Business Reviews, but basically the more genuine reviews you have, the better the ranking signals you are generating in support of your website.
Other socials signals such as the number of followers on Facebook are far less important, if they impact at all. This doesn’t mean these platforms aren’t important, it just means they don’t pass rank juice so to speak. It’s still important to insure your profiles look good, that your name address and telephone number are accurate, and that reviews are managed. Try and post to them at least one a month, although the more frequent the better.
In conclusion
If you made it this far well done- you’ve now got a solid understanding of the basic building blocks of ranking on Google. Remember though, SEO isn’t an event -it’s a process and much of what we’ve written on here we’ve only skimmed the surface of. Unless your business has the capacity to devote significant resource to develop the expertise and deploy it, this work is probably best undertaken on your behalf by a specialist agency. The reality is most retailers don’t do either, which puts them at long term competitive risk as they risk being squeezed out of an online world wherein ever-increasing numbers of consumers are turning first to research their home improvement projects.
